Operating systems miscellaneous
- Consider a uni processor system executing three tasks T1, T2 and T3, each o which is composed of an infinite sequence of jobs (or instances) which arrive periodically at intervals of 3, 7 and 20 milliseconds, respectively. The priority of each task is the inverse of its period, and the available tasks are scheduled in order of priority, with the highest priority task scheduled first. Each instance of T1, T2 and T3 requires an execution time of 1, 2 and 4 milliseconds, respectively. Given that all tasks initially arrive at the beginning of the 1st millisecond and task preemptions are allowed, the first instance of T3 completes its execution at the end of ______ milliseconds.
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
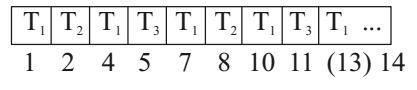
Correct Option: B

- Consider the following set of processes that need to be scheduled on a single CPU. All the times are given in milliseconds.
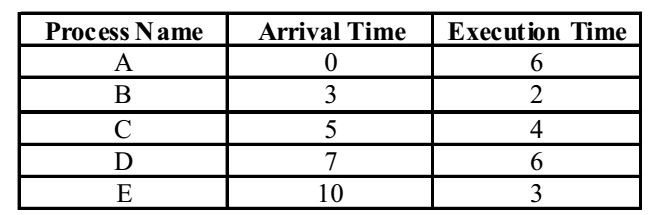
Using the shortest remaining time first scheduling algorithm, the average process turnaround time (in msec) is ____________________.
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
As we know, in the shortest remaining time first algorithm, at a given time t, process p is scheduled if its remaining execution time is minimum among all processes. (Note that this algo is applicable only when all processes declare their execution time in advance before they begin).
Now the Gantt chart for the given processes is as follows: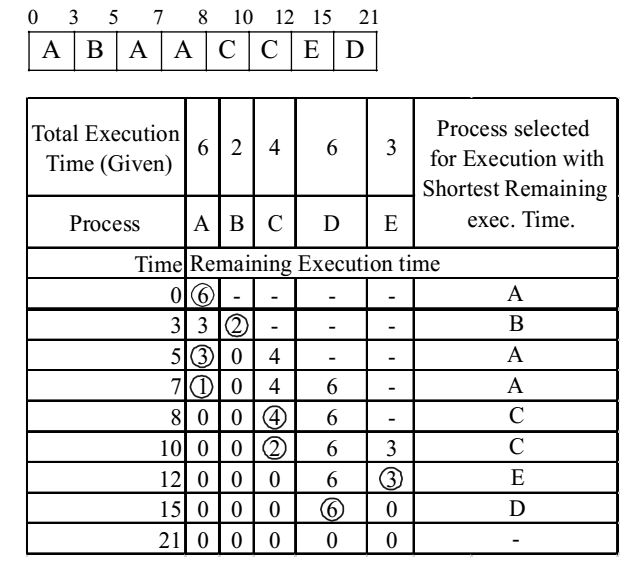
The first column of the table indicates the running time. Each entry in the table indicates the remaining execution time of that process at that time. Here a ‘–’ indicates that a process has not arrived and a ‘zero’ indicates that the process has finished. The last column indicates the process selected for execution that has shortest remaining execution time; these are marked with red circles. Using the Gantt chart, the arrival time, termination time and turnaroud time of different processes is as follows :Process Arrival Time Termination Time Turnaround Time (m sec) A 0 8 8 B 3 5 2 C 5 12 7 D 7 21 14 E 10 15 5
Total turnaround item of all processes = 36 m sec.Average turnaround time = 36 = 7.2 m sec. 5 Correct Option: A
As we know, in the shortest remaining time first algorithm, at a given time t, process p is scheduled if its remaining execution time is minimum among all processes. (Note that this algo is applicable only when all processes declare their execution time in advance before they begin).
Now the Gantt chart for the given processes is as follows:
The first column of the table indicates the running time. Each entry in the table indicates the remaining execution time of that process at that time. Here a ‘–’ indicates that a process has not arrived and a ‘zero’ indicates that the process has finished. The last column indicates the process selected for execution that has shortest remaining execution time; these are marked with red circles. Using the Gantt chart, the arrival time, termination time and turnaroud time of different processes is as follows :Process Arrival Time Termination Time Turnaround Time (m sec) A 0 8 8 B 3 5 2 C 5 12 7 D 7 21 14 E 10 15 5
Total turnaround item of all processes = 36 m sec.Average turnaround time = 36 = 7.2 m sec. 5
- Three processes A, B and C each execute a loop of 100 iterations. In each iteration of the loop, a process performs a single computation that requires tC CPU milliseconds and then initiates a single I/O operation that lasts for tio milliseconds. It is assumed that the computer where the processes execute has sufficient number of I/O devices and the OS of the computer assigns different I/O devices to each process. Also, the scheduling overhead of the OS is negligible. The processes have the following characteristics :
Process id tc tio A 100 ms 500 ms B 350 ms 500 ms C 200 ms 500 ms
The processes A, B, and C are started at times 0, 5 and 10 milliseconds respectively, in a pure time sharing system (round robin scheduling) that uses a time slice of 50 milliseconds. The time in milliseconds at which process C would complete its first I/O operation is ___________.
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
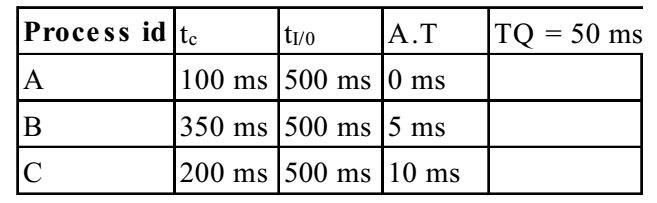
The Gantt chart for Round robin algorithm for the first iteration execution for each of the 3 processes is as follows :
After finishing tc CPU ms at time 500ms, C goes for I/O operation, that needs 500ms more, so the time at which process C would complete its first I/O operations is 500 + 500 = 1000 msCorrect Option: C

The Gantt chart for Round robin algorithm for the first iteration execution for each of the 3 processes is as follows :
After finishing tc CPU ms at time 500ms, C goes for I/O operation, that needs 500ms more, so the time at which process C would complete its first I/O operations is 500 + 500 = 1000 ms
- Consider the set of processes with arrival time (in milliseconds). CPU burst time (in milliseconds) and priority (0 is the highest priority) shown below. None of the processes have I/O burst time.
Process Arrival Time Burst Time Priority P1 0 11 2 P2 5 28 0 P3 12 2 3 P4 2 10 1 P5 9 16 4
The average waiting time (in milliseconds) of all the processes using preemptive priority scheduling algorithm is ________.
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum

Gantt chart for above problem looks like:
Waiting Time = (Completion time – Arrival time – Burst time).
∑AT = (0 + 5 + 12 + 2 + 9) = 28
∑BT = (11 + 28 + 2 + 10 + 16) = 67
∑CT = (67 + 51 + 49 + 40 + 33) = 240
Waiting time = (240 – 28 – 67) = 145Average Waiting time = 145 = 29 ms 5
Hence, 29 ms is correct answer.
Correct Option: D

Gantt chart for above problem looks like:
Waiting Time = (Completion time – Arrival time – Burst time).
∑AT = (0 + 5 + 12 + 2 + 9) = 28
∑BT = (11 + 28 + 2 + 10 + 16) = 67
∑CT = (67 + 51 + 49 + 40 + 33) = 240
Waiting time = (240 – 28 – 67) = 145Average Waiting time = 145 = 29 ms 5
Hence, 29 ms is correct answer.
- Suppose a disk has 201 cylinders, numbered from 0 to 200. At some time the disk arm is at cylinder 100, and there is a queue of disk access requests for cylinders 30, 85, 90, 100, 105, 110, 135 and 145. If Shortest-Seek Time First (SSTF) is being used for scheduling the disk access, the request for cylinder 90 is serviced after servicing ____________ number of requests.
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
Remember that in SSTF algo the request with shortest seek fine from “current Head Position” is serviced first. We prepare the following table:
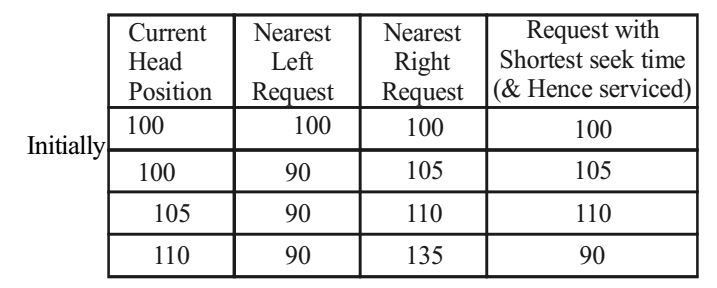
Initially Head is of 100, so it services Request for 100 itself. Then 105 is serviced because it is nearest to 100. Now as head is at 105, Request for ‘110’ is serviced as it is nearer than 90. Finally as head is on 110, out of two nearest requests viz. 90 & 135, ‘90’ is serviced since it is nearer than “135”. 80, ‘90’ is serviced after servicing 3 Requests.Correct Option: C
Remember that in SSTF algo the request with shortest seek fine from “current Head Position” is serviced first. We prepare the following table:

Initially Head is of 100, so it services Request for 100 itself. Then 105 is serviced because it is nearest to 100. Now as head is at 105, Request for ‘110’ is serviced as it is nearer than 90. Finally as head is on 110, out of two nearest requests viz. 90 & 135, ‘90’ is serviced since it is nearer than “135”. 80, ‘90’ is serviced after servicing 3 Requests.

