Municipal solid waste miscellaneous
- To determine the BOD5 of a waste water sample, 5, 10 and 50 ml aliquots of the waste water were diluted to 300 ml and incubated at 20°C in BOD bottles for 5 days.
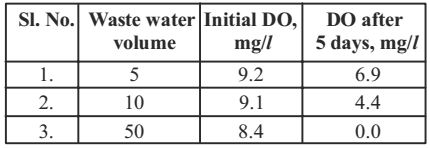
Based on the data, the average BOD5 of the wastewater is equal to
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
BOD5 = Oxygen consumed × Dilution factor
Sample 1: BOD5 = (9.2 – 6.9) × 300/5 = 138 mg/l
Sample 2: BOD5 = (9.1 – 4.4) × 300/10 = 141 mg/l
Sample 3: BOD5 = (8.4 – 0) × 300/50 = 50.4 mg/lAverage BOD = 138 + 141 + 50.4 = 109.8 mg/l 3 Correct Option: C
BOD5 = Oxygen consumed × Dilution factor
Sample 1: BOD5 = (9.2 – 6.9) × 300/5 = 138 mg/l
Sample 2: BOD5 = (9.1 – 4.4) × 300/10 = 141 mg/l
Sample 3: BOD5 = (8.4 – 0) × 300/50 = 50.4 mg/lAverage BOD = 138 + 141 + 50.4 = 109.8 mg/l 3
- 50 g of CO2 and 25 g of CH4 are produced from the decomposition of municipal solid waste (MSW) with a formula weight of 120 g. What is the average per capita green house gas production in a city of 1 million people with a MSW production rate of 500 ton/day?
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
MSW percapita = 500 × 106 = 500 g/capita. 1 × 106
120 g MSW produces 75 g green house gases (50g CO2, 25g CH4)
Therefore, 500 g MSW will produce 75/120 × 500 = 313 g green house gases.Correct Option: D
MSW percapita = 500 × 106 = 500 g/capita. 1 × 106
120 g MSW produces 75 g green house gases (50g CO2, 25g CH4)
Therefore, 500 g MSW will produce 75/120 × 500 = 313 g green house gases.
- A wastewater sample contains 10–5.6 m mol/l of OH– ions at 25°C. The pH of this sample is
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
[H–1] [OH–] = 10–14
[OH–] = 10–5.6 m mol/l
= 10–5.6 × 10–3 mol/l
= 10–8.6 mol/l∴ [H+] = 10–14 = 10–5.4mol/l 10–8.6
pH = –log[H+] = – log[10–5.4] = 5.4.Correct Option: D
[H–1] [OH–] = 10–14
[OH–] = 10–5.6 m mol/l
= 10–5.6 × 10–3 mol/l
= 10–8.6 mol/l∴ [H+] = 10–14 = 10–5.4mol/l 10–8.6
pH = –log[H+] = – log[10–5.4] = 5.4.
- The 5-day BOD of a waste water sample is obtained as 190 mg/l (with k = 0.01h–1). The ultimate oxygen demand (mg/l) of the sample will be
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
BOD5 = BOD4[1 – 10–kD.t]
BOD4 = BOD5 [1 - 10–kD.t]
kD = 0.434 k = .434 × 0.01 h–1
kDt = .434 × .01 × 5 × 24 = 0.5208BOD4 = 190 [1 - 10-0.5208]
= 271 mg/l.Correct Option: C
BOD5 = BOD4[1 – 10–kD.t]
BOD4 = BOD5 [1 - 10–kD.t]
kD = 0.434 k = .434 × 0.01 h–1
kDt = .434 × .01 × 5 × 24 = 0.5208BOD4 = 190 [1 - 10-0.5208]
= 271 mg/l.
- A horizontal flow primary clarifier treats waste water in which 10%, 60% and 30% of particles have settling velocities of 0.1 mm/s, 0.2 mm/s and 1.0 mm/s respectively. What would be the total percentage of particles removed if clarifier operates at a surface overflow rate (SOR) of 43.2 m³/m². d?
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
SOR = 43.2 m³/m²d
= 43.2 × 10³ mm/s 24 × 60 × 60
= 0.5 mm/s
30% particles has settling velocity more than SOR. So, it will settle particles with velocity lower than SOR, that will settle equals to its ratio with SOR.∴ % particles removed = 30% + 60% × 0.2 + 10 % × 0.1 = 56 % 0.5 0.5 Correct Option: B
SOR = 43.2 m³/m²d
= 43.2 × 10³ mm/s 24 × 60 × 60
= 0.5 mm/s
30% particles has settling velocity more than SOR. So, it will settle particles with velocity lower than SOR, that will settle equals to its ratio with SOR.∴ % particles removed = 30% + 60% × 0.2 + 10 % × 0.1 = 56 % 0.5 0.5

