Foundation engineering miscellaneous
- Net ultimate bearing capacity of a footing embedded in a clay stratum
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
qu = CNc + 8DNq + 0.5 BγNγ
For clay, Φ = 0 (pure cohesive)
⇒ Nq = 1, Nγ = 0
⇒ Qu = CNc + γD
∴ Qun = qu – γD
∴ = CNC + γD – γD = CNcCorrect Option: D
qu = CNc + 8DNq + 0.5 BγNγ
For clay, Φ = 0 (pure cohesive)
⇒ Nq = 1, Nγ = 0
⇒ Qu = CNc + γD
∴ Qun = qu – γD
∴ = CNC + γD – γD = CNc
- Dilatancy correction is required when a strata is
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
ng = 15 + 1 (N0 - 15) 2
N0 - SPT value after over burden pressure correction is applied.Correct Option: C
ng = 15 + 1 (N0 - 15) 2
N0 - SPT value after over burden pressure correction is applied.
- A smooth rigid retaining wall moves as shown in the sketch causing the back fill material to fail. The black fill material is homogeneous and isotropic, and obeys the Mohr-Coulomb failure criterion. The major principal stress is

-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
Retaining wall moves towards back fill ie, positive earth pressure
ie, σh > σv.Correct Option: B
Retaining wall moves towards back fill ie, positive earth pressure
ie, σh > σv.
- Likelihood of general shear failure for an isolated footing in sand decrease with
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
decreasing inter-granular packing of the sand
Correct Option: B
decreasing inter-granular packing of the sand
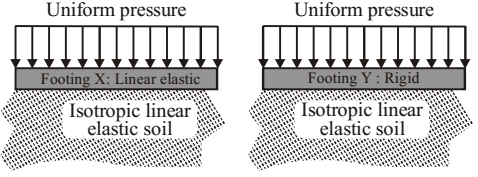
- Two geometrically identical isolated footings × (linearly elastic) and Y (rigid), are loaded identically (shown alongside). The soil reactions will.
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
be uniformly distributed for Y but not for X
Correct Option: A
be uniformly distributed for Y but not for X

