Fluid mechanics and hydraulics miscellaneous
- In a 1/50 model of a spillway, the discharge was measured to be 0.3m3 /sec. The corresponding prototype discharge in m³ /sec is
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
Qr = Qm = (Lr)5/2 Qp ⇒ 0.3 = 
1 
5/2 Qp 50
∴ Qp = 5303 m³ /sCorrect Option: D
Qr = Qm = (Lr)5/2 Qp ⇒ 0.3 = 
1 
5/2 Qp 50
∴ Qp = 5303 m³ /s
- A 15 cm length of steel rod with relative density of 7.4 is submerged in a two layer fluid. The bottom layer is mercury and the top layer is water. The height of a top surface of the rod above the liquid interface in ‘cm’ is
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
Consider buoyance of floating bodies
Sb hb = Sw x + Sm (15 – x)
⇒ 7.4 × 15 = 1.x + 13.6 (15 – x)
∴ x = 7.38 cmCorrect Option: D
Consider buoyance of floating bodies
Sb hb = Sw x + Sm (15 – x)
⇒ 7.4 × 15 = 1.x + 13.6 (15 – x)
∴ x = 7.38 cm
- A rectangular open channel of width 5.0 m is carrying a discharge of 100 m3 /s. The Froude number of the flow is 0.8. The depth of flow (in m) in the channel is
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
Fr = V √gy V = Q = Q A By = Q By√gy = Q B√gy3/2 ∴ y = 
Q 
2/3 B√g. Fr = 
100 
2/3 = 4 m . 5 × √9.81 × 0.8
Correct Option: A
Fr = V √gy V = Q = Q A By = Q By√gy = Q B√gy3/2 ∴ y = 
Q 
2/3 B√g. Fr = 
100 
2/3 = 4 m . 5 × √9.81 × 0.8
- A triangular open channel has a vertex angle to 90° and carries flow at a critical depth of 0.30 m. The discharge in the channel is
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
At flow at critical depth, Q is maximum.
Q2 = A3 g T
Q = √(A3 .g) / TA = 1 × 2y × y = y2 2
T = 2y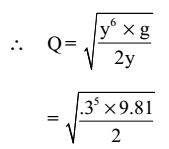
≈ 0.1 m3 / s.
Correct Option: B
At flow at critical depth, Q is maximum.
Q2 = A3 g T
Q = √(A3 .g) / TA = 1 × 2y × y = y2 2
T = 2y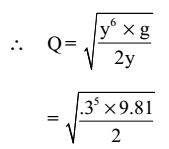
≈ 0.1 m3 / s.
- A solids sphere (diameter 6 mm) is rising through oil (mass density 900 kg/m3, dynamic viscosity 0.7 kg/ms) at a constant velocity of 1 cm/s. What is the specific weight of the material from which the sphere is made? (Take g = 9.81 m/s2)
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
In dynamic equilibrium conditions, Upward force = Downward force
⇒ Buoyant force = weight of sphere + Drag force.ρoil. v.g = ρsphere. v.g + 1 cd.ρsphere.A V2 2
ρoil = 900 kg/m3
V = Surface volume of sphere= 4 πR3 3 R = 6 × 10-3 = 0.03 m 2 ∴ V = 4 π × (0.003)3 = 1.31 × 10-7 m3 3 Re = V.D υoil = V.D = 0.01 × 0.006 
μ 
(0.7 / 900) e
= 0.0771 < 1∴ CD = 24 Re
A = πR2
= π × (0.003)2
= 0.283 × 10-4 m2
V = 0.01 m / s∴ 900 × 1.131 × 10-4 = ρsphere × 1.131 × 10-7 × 9.81 + 
1 × 311.28 × 900 × 0.283 × 10-4 × (0.01)2 
2
∴ ρsphere = 543.37 kg / m3
⇒ γsphere = 543.4 × 9.81 N / m3 ≈ 5.33 kN / m3
Correct Option: B
In dynamic equilibrium conditions, Upward force = Downward force
⇒ Buoyant force = weight of sphere + Drag force.ρoil. v.g = ρsphere. v.g + 1 cd.ρsphere.A V2 2
ρoil = 900 kg/m3
V = Surface volume of sphere= 4 πR3 3 R = 6 × 10-3 = 0.03 m 2 ∴ V = 4 π × (0.003)3 = 1.31 × 10-7 m3 3 Re = V.D υoil = V.D = 0.01 × 0.006 
μ 
(0.7 / 900) e
= 0.0771 < 1∴ CD = 24 Re
A = πR2
= π × (0.003)2
= 0.283 × 10-4 m2
V = 0.01 m / s∴ 900 × 1.131 × 10-4 = ρsphere × 1.131 × 10-7 × 9.81 + 
1 × 311.28 × 900 × 0.283 × 10-4 × (0.01)2 
2
∴ ρsphere = 543.37 kg / m3
⇒ γsphere = 543.4 × 9.81 N / m3 ≈ 5.33 kN / m3

