Breathing and Exchange of Gases
- Listed below are four respiratory capacities (i–iv) and four jumbled respiratory volumes of a normal human adult:
Respiratory Respiratory capacities volumes
(i) Residual volume 2500mL
(ii) Vital capacity 3500mL
(iii) Inspiratory reserve 1200mL volume
(iv) Inspiratory capacity 4500mL
Which one of the following is the correct matching of two capacities and volumes?
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
The correct matching of respiratory capacities with their respiratory volumes are:
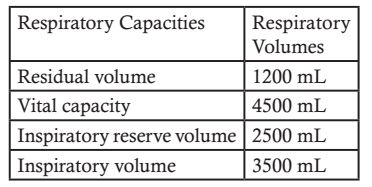
Correct Option: C
The correct matching of respiratory capacities with their respiratory volumes are:

- The alveolar epithelium in the lungs is
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
The very thin alveolar wall (about 0.0001 mm) is composed of moist, non– ciliated, squamous epithelial cells
Correct Option: B
The very thin alveolar wall (about 0.0001 mm) is composed of moist, non– ciliated, squamous epithelial cells
- Skin is an accessory organ of respiration in
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
Frog has lungs as its main respiratory organs but during hibernation & aestivation and when in water it respires through skin.
Correct Option: B
Frog has lungs as its main respiratory organs but during hibernation & aestivation and when in water it respires through skin.
- Air is breathed through
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
The pathway of inhaled air is - Nostrils → pharynx (common passage for food & air) → larynx (voice box) → trachea (the wind pipe) → bronchi (2 for each side lungs) → bronchioles (give rise to alveolar ducts) → alveoli (the exchange site for gases in the form of small sacs or pouches).
Correct Option: C
The pathway of inhaled air is - Nostrils → pharynx (common passage for food & air) → larynx (voice box) → trachea (the wind pipe) → bronchi (2 for each side lungs) → bronchioles (give rise to alveolar ducts) → alveoli (the exchange site for gases in the form of small sacs or pouches).
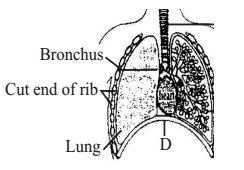
- The figure shows a diagrammatic view of human respiratory system with labels A, B, C and D. Select the option which gives correct identification and main function and/or characteristics.
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
Alveoli are very thin, irregular walled bag like structures for gaseous exchange. Tracheae bronchi and bronchioles are supported by incomplete cartilaginous rings. Double layered pleural membrane surrounds the lungs with pleural fluid between them. It reduces friction on the lung surface.
Correct Option: B
Alveoli are very thin, irregular walled bag like structures for gaseous exchange. Tracheae bronchi and bronchioles are supported by incomplete cartilaginous rings. Double layered pleural membrane surrounds the lungs with pleural fluid between them. It reduces friction on the lung surface.

