Plant Kingdom
- Zygotic meiosis is characteristic of :
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
Chlamydomonas has haplontic life cycle hence shows zygotic meiosis.
Correct Option: C
Chlamydomonas has haplontic life cycle hence shows zygotic meiosis.
- Sexual reproduction involving fusion of two cells in Chlamydomonas is
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
Isogamy refers to a form of sexual reproduction involving gametes of the same size. Since both gametes look alike, they cannot be classified as “male” or “female.” Instead, organisms undergoing isogamy are said to have different mating types, most commonly noted as “+” and “–” strains. Fertilization occurs when “+” and “–” strain gametes fuse to form a zygote. There are several types of isogamy. Both gametes may be flagellated and thus motile. This type mating occurs in algae such as Chlamydomonas.
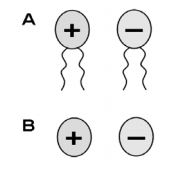
A. Isogamy of motile cells
B. Isogamy of non-motile cellsCorrect Option: A
Isogamy refers to a form of sexual reproduction involving gametes of the same size. Since both gametes look alike, they cannot be classified as “male” or “female.” Instead, organisms undergoing isogamy are said to have different mating types, most commonly noted as “+” and “–” strains. Fertilization occurs when “+” and “–” strain gametes fuse to form a zygote. There are several types of isogamy. Both gametes may be flagellated and thus motile. This type mating occurs in algae such as Chlamydomonas.

A. Isogamy of motile cells
B. Isogamy of non-motile cells
- The common mode of sexual reproduction in Chlamydomonas is
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
In Chlamydomonas, sexual reproduction takes place through :
1. Isogamy : Fusion of 2 similar gametes.
2. Anisogamy : Fusion between morphologically similar but physiologically different gametes.
3. Oogamy : Fusion between two dissimilar gametes.
4. Hologamy : Fusion of two young cells. Most common mode is isogamy.Correct Option: A
In Chlamydomonas, sexual reproduction takes place through :
1. Isogamy : Fusion of 2 similar gametes.
2. Anisogamy : Fusion between morphologically similar but physiologically different gametes.
3. Oogamy : Fusion between two dissimilar gametes.
4. Hologamy : Fusion of two young cells. Most common mode is isogamy.
- The product of conjugation in Spirogyra or fertilization of Chlamydomonas is
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
In both the members of green algae, Spirogyra and Chlamydomonas, gametes fuse to form zygote which develops into a thick walled resting zygospore. Zoospore is asexual spore while ospore is sexual spore.
Correct Option: A
In both the members of green algae, Spirogyra and Chlamydomonas, gametes fuse to form zygote which develops into a thick walled resting zygospore. Zoospore is asexual spore while ospore is sexual spore.
- Pyrenoids are the centres for formation of
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
In cell biology, pyrenoids are centers of carbon dioxide fixation within the chloroplasts of algae and hornworts. Pyrenoids are not membrane-bound organelles, but specialized areas of the plastid that contain high levels of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/ oxygenase (RUBISCO). RUBISCO fixes carbon dioxide by adding it to the 5-carbon sugar-phosphate, ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate, yielding two molecules of the 3-carbon compound, 3-phosphoglycerate. In a competing reaction, the enzyme uses oxygen to break down ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate to phosphoglycolate and 3-phosphoglycerate, with no net fixation of carbon.
Correct Option: D
In cell biology, pyrenoids are centers of carbon dioxide fixation within the chloroplasts of algae and hornworts. Pyrenoids are not membrane-bound organelles, but specialized areas of the plastid that contain high levels of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/ oxygenase (RUBISCO). RUBISCO fixes carbon dioxide by adding it to the 5-carbon sugar-phosphate, ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate, yielding two molecules of the 3-carbon compound, 3-phosphoglycerate. In a competing reaction, the enzyme uses oxygen to break down ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate to phosphoglycolate and 3-phosphoglycerate, with no net fixation of carbon.

