Ecosystem
- Which of the following pairs is a sedimentary type of biogeochemical cycle?
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
Biogeochemical cycles: Two types: (a) Gaseous: Biogenetic materials involved in circulation are gases eg. N2, O2, CO2 etc. (b) Sedimentary: Biogenetic materials involved in circulation are nongaseous eg. P, Ca, S etc. forms rocks.
Correct Option: B
Biogeochemical cycles: Two types: (a) Gaseous: Biogenetic materials involved in circulation are gases eg. N2, O2, CO2 etc. (b) Sedimentary: Biogenetic materials involved in circulation are nongaseous eg. P, Ca, S etc. forms rocks.
- Both, hydrarch and xerarch successions lead to:
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
Hydrarch succession takes place in wet areas and xerarch succession respectively, which takes place in dry areas. So, both hydrarch and xerarch successions leads to medium water conditions.
Correct Option: A
Hydrarch succession takes place in wet areas and xerarch succession respectively, which takes place in dry areas. So, both hydrarch and xerarch successions leads to medium water conditions.
- Identify the possible link “A” in the following food chain:
Plant ? insect - frog ? “A” ? Eagle
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
NA
Correct Option: C
NA
- Given below is an imaginary pyramid of numbers. What could be one of the possibilities about certain organisms at some of the different levels?
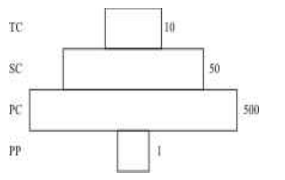
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
NA
Correct Option: A
NA
- Which one of the following is not a function of an ecosystem?
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
Four important functional aspects of the ecocystem are
(i) Productivity
(ii) Decomposition,
(iii) Energy flow and
(iv) Nutrient cycling.Correct Option: D
Four important functional aspects of the ecocystem are
(i) Productivity
(ii) Decomposition,
(iii) Energy flow and
(iv) Nutrient cycling.

